13: Deploying Applications
When you are finished developing and testing your project, you can deploy the runtime application for use by end-user clients. Projects can be deployed to run locally on a stand-alone computer or embedded device, as well as in a client-server distributed architecture or on the cloud. This chapter discusses the various methods for deploying these applications.
The following sections discuss the issues in deploying the runtime application:
- "Local and Distributed Systems" explains the various types of installation that FactoryStudio supports.
- "Product Installation on the Target Computer" describes how to install FactoryStudio on a single computer or on the servers and clients in a distributed system.
- "License and Project Settings Verification" discusses how to ensure that the settings for your project are correct for the license that you have.
- "Installing the Project Files" explains how to install your project on a computer other than the one on which it was configured.
- "Setup the Server to Start the Runtime" presents the various ways you can configure your project for manual or automatic startup.
- "Remote Client Users Setup" describes the ways of setting up your project for access using a Windows rich, smart, or web client or an iOS client.
- "Deploying Redundant Systems" explains how to setup your project to use a second, redundant server for hot backup.
 Local and Distributed Systems
Local and Distributed Systems
.i.clients:described;
.i.servers:described;
.i.runtime components, described;
FactoryStudio supports many deployment scenarios such as:
- Embedded devices with no local user interface.
- Stand-alone panels or computers with local user interface.
- Distributed systems with many client stations accessing a server.
- Redundant servers with multiple users connected.
The setup procedures for each scenario have many common steps. For all the systems, even the stand-alone installations, FactoryStudio makes use of a client-server architecture.
The server components are the project file and the modules that run the server side tasks, such as data-acquisition, alarms and data logging. The client components are the graphical user interfaces and related scripts.
When you have a local or stand-alone project the server and the client components run on the same machine.
The client technologies used by FactoryStudio simplify deployment, since you have to install the project only on the server computer. All the client stations will use the project from the server.
In order to setup the server components or stand-alone configurations refer to the following sections: "Product Installation on the Target Computer", "License and Project Settings Verification", and "Installing the Project File".
The client setup can be slightly different according to its type. FactoryStudio supports the following client technologies:
- Windows rich clients
- Windows smart clients
- Windows web-based clients
- iOS clients
For more on these client types see "Remote Client Users Setup".
If you need to use Active-X, COM, and JavaScript, you can access the runtime application using the DataAccess API, which is a COM interface to provide integration with Active-X, JavaScript on web pages, or legacy programming languages such as VBScript. Contact support for assistance.
For redundant scenarios see "Deploying Redundant Systems".
 Product Installation on the Target Computer
Product Installation on the Target Computer
The server computer on distributed systems, or the standalone computer if used, must have FactoryStudio installed and licensed. The section "Installing FactoryStudio" in the "Getting Started" guide describes the standard way to install and license FactoryStudio. All servers and clients require the .NET framework, version 4.0 or higher.
When you are not using components that require the setup of the Windows Registry, such as the OPC components, you also just copy the product files without running any installation. This is especially useful for embedding the software on devices. If needed, you may remove project examples or engineering components and add custom protocols.
On distributed systems, the client computers don't require a license, they just need to be allowed to connect with the server based on number of runtime users enabled on the server. For more information on the client setup, see "Remote Client Users Setup", below.
If the system will have remote users, a web server, either TWebServer or IIS, must be installed and running on the server computer.
 License and Project Settings Verification
License and Project Settings Verification
A FactoryStudio project is created targeting one specific Product Family and Product Model, as defined on the Info > Project > Settings page.
It is necessary to ensure that the license on the server computer is greater than or equal to the requirements of the project, by reviewing the following checklist:
- The Family defined in the license must be the same as the family in the project or a higher hierarchy family.
- Enterprise licenses can run all projects (Enterprise, HMI and OPCServer)
- HMI licenses can run HMI and OPC Server projects
- OPCServer licenses can run only OPC server projects
- Express licenses or projects are not authorized for production environments.
- The Model in the license must support a number of communication points equal to or greater than the requirements of the project that will run on the server computer.
- The License Type on the target computer must be Engineering or Runtime. Licenses of type DEV (Development) are only for the internal work of System Integrators and may not be used in production environments.
- If the project requires any additional interfaces, such as the OSIsoft(tm) PI System, or IEC protocols, the license on the target computer must be enabled for those interfaces.
- The number of remote clients enabled must meet the project requirements.
For more Information about product and license models refer to Chapter 14, "Versions and Licenses".
 Installing the Project File
Installing the Project File
A project is installed as a single file, either the main configuration file (with extension "tproj") or a read-only file (with extension "trun") if you have created one.
The Project Management utility allows you to connect with remote servers and download the project file to remote computers.
Although that one file contains the entire project configuration, you should use the following checklist to ensure that any external dependencies are also taken care of.
- If the folder structure on the production computer is not the same as on the computer you used for development, make sure that all the places you have file paths in your project are mapped correctly to the production computer. FactoryStudio has many features and macros to define paths relative to the project location, product installation or execution path; whenever possible avoid using fixed path locations in your projects.
- Any external WPF controls should also be copied to the target computer. For remote web access those files should be located in the folder WpfControl and the utility to update the web manifest must be executed.
- If the application references external DLL or .NET assemblies, ensure they are available and at the correct paths on the target computer.
- If the project uses Retentive values, you must decide if the target computer will create a new Retentive database or if you will copy one with some predefined values.
- Enable the firewall to allow remote clients. Ports 3101 for startup (optionally port 3201 to Test Mode). For web and iOS clients, data web services are enabled on port 80.
- If the application uses external DLLs, WpfControls, configuration files or embedded databases, make sure you copy those files to the target machine and double check if the PATHNAMES you used in the project configuration are compatible.
 Setup the Server to Start the Runtime
Setup the Server to Start the Runtime
You can run the project in any of the following ways:
- Start manually. From the FactoryStudio main window and project list, right-click the project and select Run Project.
- Start manually. When configuring the project, go to Run > Startup and click Run Startup.
- Start the project automatically, which is the best option for production environments.
The best way to define an automated startup of the product, it is to use the configuration interface available on the Project Management tools, at the Server tab.
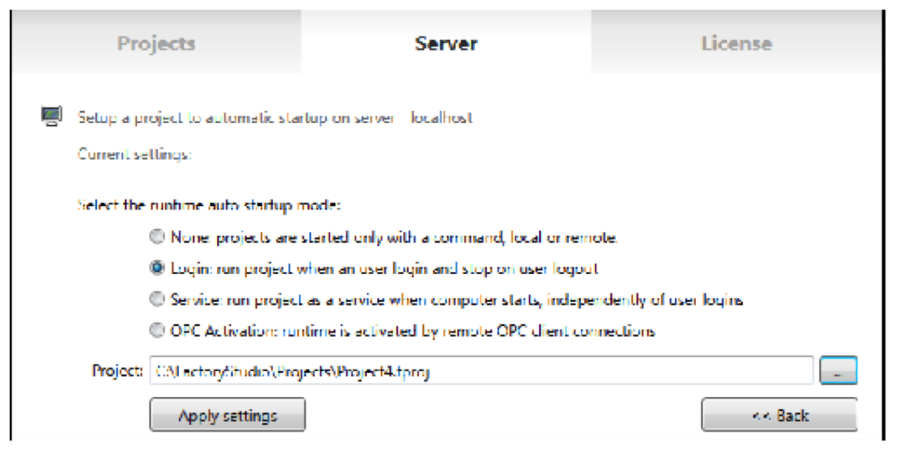
We recommend that you start manually during project development or installation, where an operator is needed during the startup process. When your project is setup for production, automated startup is more suitable.
You should use the login option, the startup shortcut, when testing the project, or in scenarios where the application will always run in the same Windows user profile.
Use the Windows Service on production servers when you need different Windows users to login to the computer, while keeping the server side runtime components running at all times.
We also support OPC client activation, in order to be in full OPC compliance, but we don't recommend its use, because, as a good practice principle, it is not desirable to allow the status of remote client connections to control whether a server side application is running.
The following sections will describe what those automated settings are doing in case, for some reason, you need to setup those startup settings without using the configuration tools.
 Using a Shortcut on Windows Startup
Using a Shortcut on Windows Startup
.i.servers:automatically starting with a shortcut;
.i.automatically starting applications on the server;
.i.Windows:automatically starting applications on;
.i.shortcut, using to automatically start applications;
You can configure a Windows server to automatically start a project using a startup shortcut. The startup shortcut starts the application when a user logs in to Windows, and the application stops running when the user logs off of Windows.
This procedure is automatically executed by the system when the startup mode is selected, as described above. This section will explain how to manually setup those shortcuts.
The Project runtime startup is executed by the program TStartup.exe.
When using this example, make sure to change the installation path and version of FactoryStudio to the installation on your computer.
The project is started from a command line window. The following command line parameters are available:
/project: Project Path and Name between double quotes
/username: (optional), username that will be used to start the server , if you do not specify, the user guest will be used.
/redundancy: indicates that the server redundancy is being used (requires ip1 and ip2)
/ip1: IP Address of the Primary FactoryStudio Server
/port1: TCP port of the Primary FactoryStudio Server
/ip2: IP Address of the Secondary FactoryStudio Server
/port2: TCP port of the Secondary FactoryStudio Server
/viewonly: indicates that the project is in view only mode
/wa: indicates that the project uses Windows Authentication
The modules that will be started are configured in the project, at Run > Startup.

Examples:
"C:\Program Files\Studio\fs-2018.1\TStartup.exe"
/project:"C:\Studio Projects\Project1.tproj"
"C:\Program Files\Studio\fs-2018.1\TStartup.exe"
/project:"C:\Studio Projects\Project1.tproj" /port1:3101
Server Redundancy:
"C:\Program Files\Studio\fs-2018.1\TStartup.exe" /project:"C:\Studio Projects\Project1.tproj" /username:Administrator /redundancy /ip1:192.168.1.1 /port1:3101 /ip2:192.168.1.2 /port2:3101
Creating the shortcut
Go to Start > All Programs, right-click the Startup folder, and select Open.
- In the Startup folder, right-click and select New > Shortcut.
- In the Create Shortcut window, paste into the field that displays.
- If you are not using redundancy, delete the redundancy part of the text.
In the examples below, be sure to change the installation path and version of FactoryStudio to the installation on your computer.
- Type or paste the full command line, for example: "C:\Program Files\Studio\fs-2018.1\TStartup.exe" /project:"C:\Studio Projects\Project1.tproj"
- Click Next.
- Enter a name for the shortcut.
- Click Finish.
When you restart the computer next, the project will start automatically.
 Using a Windows Service to Startup
Using a Windows Service to Startup
.i.servers:automatically starting application as a service;
.i.automatically starting applications on the server;
.i.Windows:automatically starting applications on;
.i.service, using to automatically start applications;
You can configure a Windows server to automatically start a project when the computer starts using a Windows Service. The Windows Service starts the application as soon as the computer is powered on and the Windows Operating System starts, even if no user has logged in to Windows.
This procedure is automatically executed by the system when selected for startup mode, as described above. This section will explain how to set it up manually.
These methods do not start the client (user interface with the displays). To automate the client startup, see "Automatically Starting Windows Clients", below.
Use the Windows Service only on production servers that you are not using as engineering stations, and only if you need the ability to differentiate Windows users logging in while the project is running.
The first several steps of the procedure below are required to let you set up the Windows Service.
To run your application as a Windows Service:
The whole command line should look something like this:
"C:\ProgramFiles(x86)\Tatsoft\FactoryStudio\fs-2018.1.1\ tStartup.exe" /project:C:\Factory Studio Projects\ <project_name>.tproj /username:<username>
- Leave the text file open for use in step 10.
- From the command line prompt, go to the <.NET Framework Install Path> and execute the following command:
installutil <InstallPath>\<fs-version>\TStartupAsService.exe
Example: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727>installutil C:\Program files\Tatsoft\FactoryStudio\fs-2018.1\ TStartupAsService.exe
 Copy and paste the command you created in the text file.
Copy and paste the command you created in the text file.- In the Windows Registry, set up the parameters on:
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\ TStartup\ImagePath"
Example: "C:\\tatsoft\fs-2018.1\TStartupAsService.exe" "/project:C:\FactoryStudio Projects\Project1.tproj"
- In the Windows Services (Administrative Tools), set "TStartup Service" to Automatic, so the selected project will start when the computer starts.
 Remote Client Users Setup
Remote Client Users Setup
 Windows Rich Clients
Windows Rich Clients
.i.deploying:Windows rich clients;
.i.rich clients, deploying;
.i.Windows clients:deploying rich clients;
.i.clients:configuring for deployment;
Rich clients are client applications that do a significant amount of processing on the client rather than on the server. You can deploy your application for use by Windows rich clients.
Table 1 describes how the rich client deployment works.
 Windows rich client deployment Windows rich client deployment
| |
Installation | Install FactoryStudio on the client computer. See "Installing FactoryStudio" in the "Getting Started" guide. |
How to start | Run the TRichClient.exe program. For an example of how to automatically start the client when a user logs in to Windows, see "Automatically Starting Windows Clients" in the previous section. |
Execution | The project runs in its own window. It allows very strong user security, including the ability to disable Windows task-switch, according to the login on the running project.
When running the TRichClientt.exe on 64-bit machines, the application runs in 64-bit native code. If you need to run the 32-bit version, for instance to ensure compatibility with legacy COM and Active-X components, you can use the TRichClient32.exe program. |
Communication | Communicates with the server using the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) (port configurable, default 3101). |
 Windows Smart Clients
Windows Smart Clients
.i.deploying:Windows smart clients;
.i.smart clients, deploying;
.i.Windows clients:deploying smart clients;
.i.clients:configuring for deployment;
Smart clients are client applications that behave like rich clients, but either run from the web or can be installed painlessly with a single click. You can deploy your application for use by Windows smart clients.
The smart client runs like the rich client, that is, they work the same way, but the smart client uses ClickOnce™ installation. This technology lets you have the same functionality as the rich client, but without having to install FactoryStudio on your computer.
The first time you access the application, the system automatically downloads the necessary components to run the application. The next time you access the application, the system verifies if the local cache is the same version of the application that is on the server, and if necessary, updates the local cache before running the application. If the version is the same, the application starts immediately.
Table 2 describes how the smart client deployment works.
 Windows smart client deployment Windows smart client deployment
| |
Installation | No installation required. You just need .NET Framework 4.0 and Internet Explorer 8.0 or later on the client computer.
The first time you start the application, it will automatically download the required components from the server. Every time the application starts, it verifies automatically if a new version is available on the server. |
How to start | From Internet Explorer (or a shortcut) go to the URL:
http://<ServerIPAddressorName>/fs-2014.1/ TSmartClient.application
For an example of how to automatically start the client when a user logs in to Windows, see "Automatically Starting Windows Clients" in the previous section. |
Execution | Runs exactly the same as the rich client. The functionality of the rich client and the smart client are the same; only the installation and activation methods are different. |
Communication | Communicates with the server using WCF (port configurable, default 3101). |
 Windows Web Clients
Windows Web Clients
.i.deploying:Windows web clients;
.i.web clients, deploying;
.i.Windows clients:deploying web clients;
.i.clients:configuring for deployment;
A web client accesses the application using a web browser. You can deploy your application for use by Windows web clients.
Table 3 describes how the web client deployment works.
 Windows web client deployment Windows web client deployment
| |
Installation | No installation required. You just need .NET Framework 4.0 and Internet Explorer 8.0 or later on the client computer.
The first time you start the application, will automatically download from the server the required components. Every time the application starts, it verifies automatically if a new version is available on the server. |
How to start | From Internet Explorer (or a shortcut) go to the URL:
http://<ServerIPAddressorName>/fs-2014.1 /TWebClient.Xbap
For an example of how to automatically start the client when a user logs in to Windows, see "Automatically Starting Windows Clients" in the previous section. |
Execution | Runs inside a web browser window using "Partial Trust" (Sandbox Security). |
Communication | Communicates with the server using HTTP or HTTPS (port 80). |
 Automatically Starting Windows Clients
Automatically Starting Windows Clients
You can create a shortcut to the appropriate executable, depending on the client type, to automatically start the application on a Windows client. You can create the shortcut on the desktop or put it into the Startup folder, as described below.
For the web client, you can also configure the application as the home page in Internet Explorer.
To begin, Go to Start > All Programs, right-click the Startup folder, and select Open to open the Startup folder.
- In the Startup folder, right-click and select New > Shortcut.
- In the Create Shortcut window, paste into the field that displays.
- If you are not using redundancy, delete the redundancy part of the text.
- Do one of the following:
- For a rich client—At the beginning of the command line, enter or paste the full path to the FactoryStudio installation folder and put quotes around it. It should look something like this: "C:\Program Files (x86)\Tatsoft\FactoryStudio\fs-2014.1.3\ TRichClient.exe" /ip1:<IP_address>
- For a smart or web client—At the beginning of the command line, enter or paste the full path to the Internet Explorer installation folder and put quotes around it. It should look something like this: "C:\Program Files (x86)\Internet Explorer\iexplorer.exe" http:<IP_address>/fs-2014.1/TSmartClient.application "C:\Program Files (x86)\Internet Explorer\iexplorer.exe" http:<IP_address>/fs-2014.1/TWebClient.Xbap
- Click Next.
- Enter a name for the shortcut.
- Click Finish.
When you next restart the computer, the project will start automatically.
 iOS Clients
iOS Clients
.i.deploying:iOS
.i.iOS:deploying;
.i.clients:configuring for deployment;
You can deploy your application for use by iOS clients: iPad, iPhone, and iTouch. For other tablet devices, contact support.
Table 4 describes how the iOS deployment works.
 iOS deployment iOS deployment
| |
Installation | Install the SCADA HMI Client app from the Apple Store. |
How to start | Start the SCADA HMI Client app and follow the initial setup options. |
Execution | On iOS, it runs natively, thus providing higher performance, enhanced security, and access to native graphical components, compared to other applications using Terminal Client, Remote Desktop, or HTML web. |
Communication | Communicates with the server by calling a web service using port 80. The server must be on the same VPN or local network as the iOS device, or it can be a public IP address, as long as HTTP access is enabled. |
To deploy your project on an iOS device:
 Deploying Redundant Systems
Deploying Redundant Systems
.i.configuring:redundancy;
.i.projects:configuring redundancy for;
.i.redundancy:configuring;
You can configure application redundancy by configuring two computers as servers. One computer will be the primary, and the other will be the secondary or hot standby. If the primary computer or connection to the computer fails, the system automatically fails over to the secondary computer.
If you selected HMI as the Product Family, the redundancy configuration is not available.
To configure redundancy:
- Go to Info >Project > Redundancy.
Enter or select the information, as needed.
Field | Description |
Enable Configuration | Select to enable the redundancy configuration. |
Primary Server IP and Port | Enter the IP address and port of the primary server. |
Secondary Server IP and Port | Enter the IP address and port of the secondary server. |
On Primary Startup | Select the option you want. |
Historian Replication | Select how to handle historian replication. |
Connection Timeout | Connection timeout time, in seconds, to switch to secondary server. |
Server Command Line | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to Clipboard to copy the command for use. |
Rich Client Command | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to copy the command for use. |
Smart Client URL | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to copy the command for use. |
Web Client URL | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to copy the command for use. |
To automatically start the application on a Windows client:
- Go to Info > Project > Redundancy.
- Enter or select the information, as needed.
Field | Description |
Enable Configuration | Select to enable the configuration. |
Primary Server IP and Port | Enter the IP address and port of the primary server. |
Secondary Server IP and Port | Enter the IP address and port of the secondary server, if any. |
On Primary Startup | Select the option you want. |
Historian Replication | Select how to handle historian replication. |
Connection Timeout | Connection timeout time, in seconds, to switch to secondary server. |
Rich Client Command | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to copy the command for use. |
Smart Client URL | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to copy the command for use. |
Web Client URL | Read-only field populated based on the fields above. Click Copy to copy the command for use. |
- Click the Copy button next to the type of client you want to start automatically.

